| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
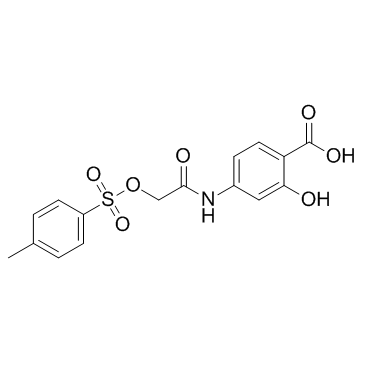 |
S3I-201
CAS:501919-59-1 |
|
 |
Leptin (human), (recombinant)
CAS:177404-21-6 |
|
 |
Hydrocortisone
CAS:50-23-7 |
|
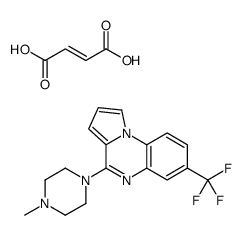 |
CGS-12066 maleate
CAS:1350965-83-1 |
|
 |
Leptin (mouse), (recombinant)
CAS:181030-10-4 |