| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
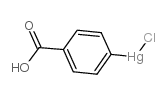 |
p-chloromercuribenzoic acid
CAS:59-85-8 |
|
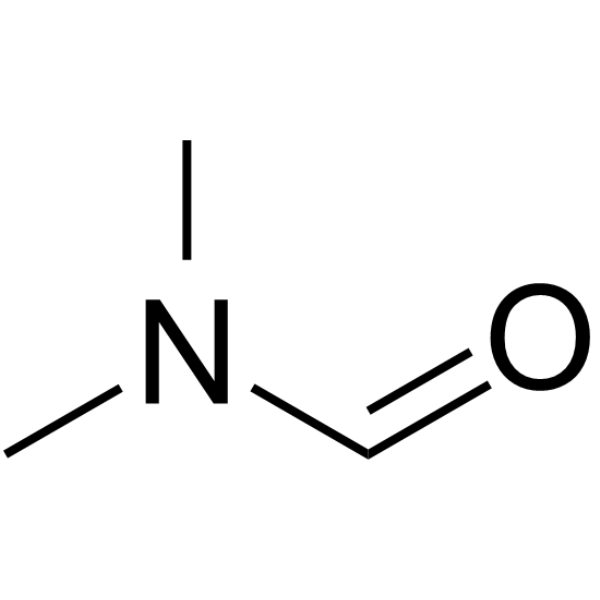 |
N,N-Dimethylformamide
CAS:68-12-2 |
|
 |
1-Naphthyl acetate
CAS:830-81-9 |