| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
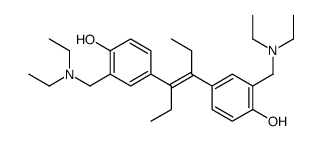 |
NSC 33994
CAS:82058-16-0 |
|
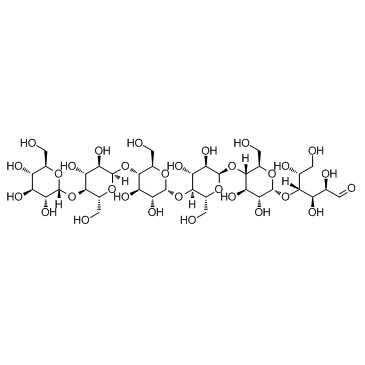 |
Maltohexaose
CAS:34620-77-4 |
|
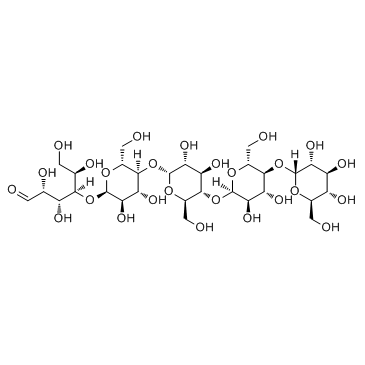 |
Maltopentaose
CAS:34620-76-3 |
|
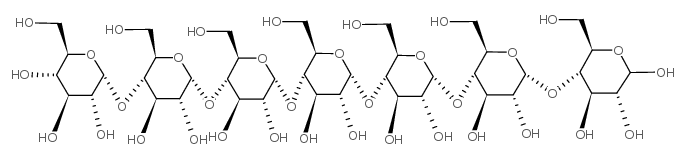 |
Maltoheptaose
CAS:34620-78-5 |