| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
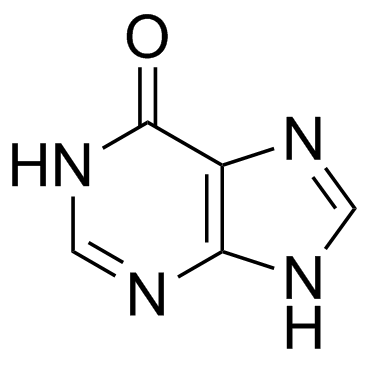 |
Hypoxanthine
CAS:68-94-0 |
|
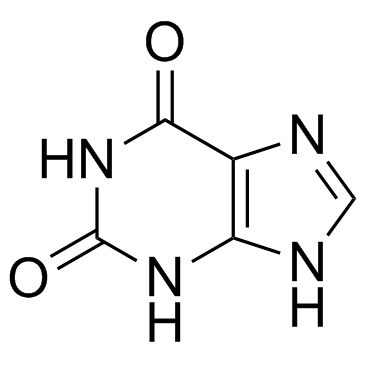 |
2,6-Dihydroxypurine
CAS:69-89-6 |
|
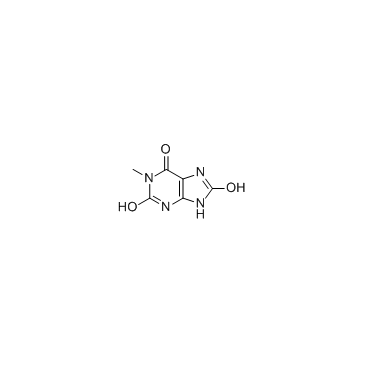 |
1-Methyluric acid
CAS:708-79-2 |
|
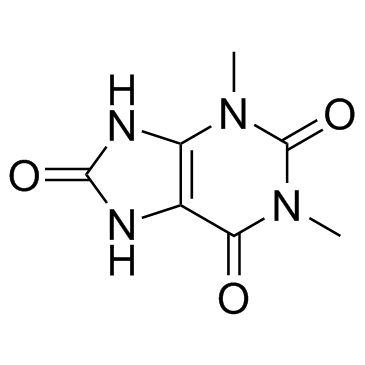 |
1,3-Dimethyluric acid
CAS:944-73-0 |