| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
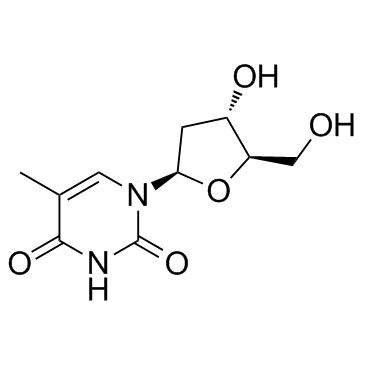 |
Thymidine
CAS:50-89-5 |
|
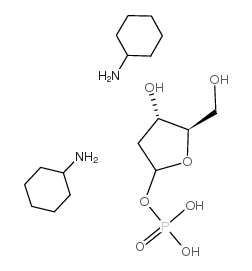 |
2-DEOXY-ALPHA-D-RIBOSE 1-PHOSPHATE BIS(CYCLOHEXYLAMINE) SALT
CAS:102783-28-8 |
|
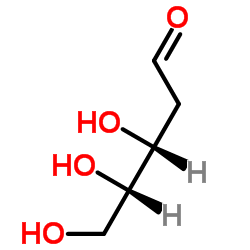 |
2-Deoxy-D-Ribose
CAS:18546-37-7 |