| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
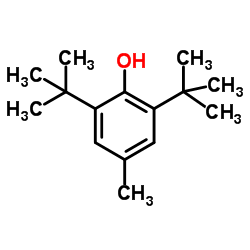 |
Butylated hydroxytoluene
CAS:128-37-0 |
|
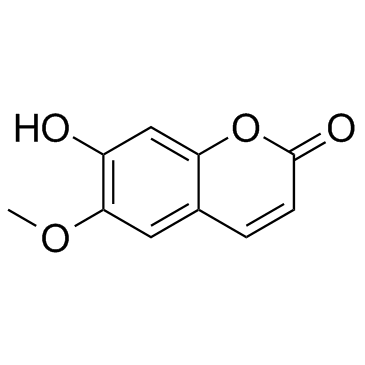 |
Scopoletin
CAS:92-61-5 |
|
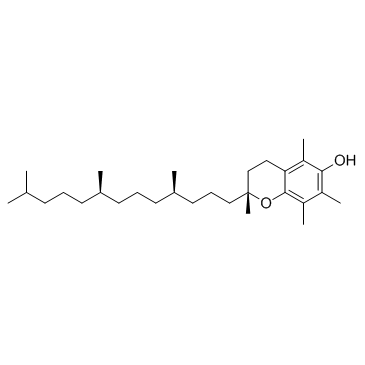 |
DL-alpha-Tocopherol
CAS:59-02-9 |
|
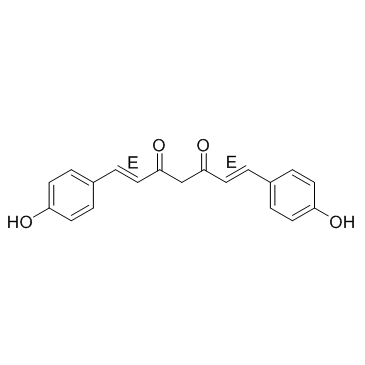 |
Bisdemethoxycurcumin
CAS:33171-05-0 |