| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
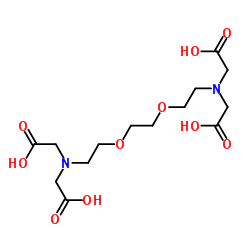 |
EGTA
CAS:67-42-5 |
|
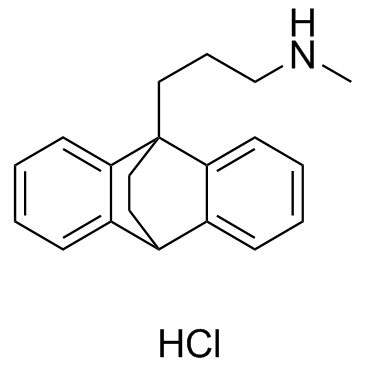 |
Maprotiline Hydrochloride
CAS:10347-81-6 |