| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
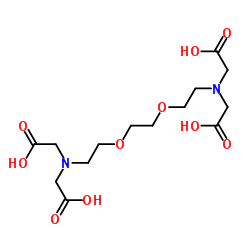 |
EGTA
CAS:67-42-5 |
|
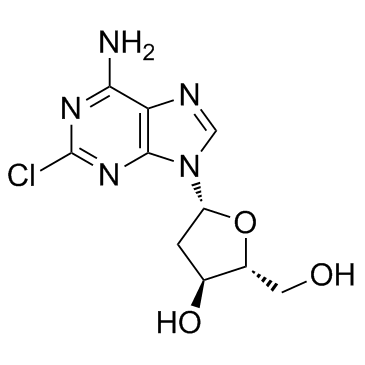 |
Cladribine
CAS:4291-63-8 |
|
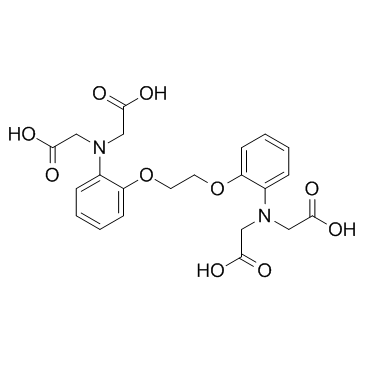 |
BAPTA
CAS:85233-19-8 |