| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
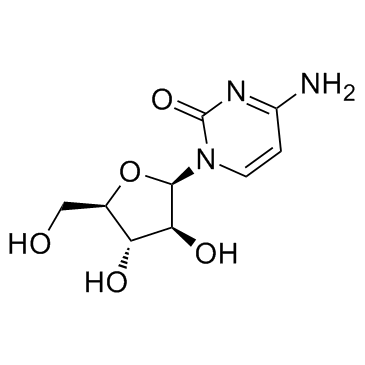 |
Cytarabine
CAS:147-94-4 |
|
 |
3-Methyladenine
CAS:5142-23-4 |
|
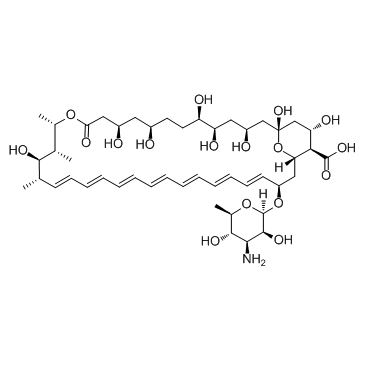 |
Amphotericin B
CAS:1397-89-3 |
|
 |
DL-O-Phosphoserine
CAS:17885-08-4 |
|
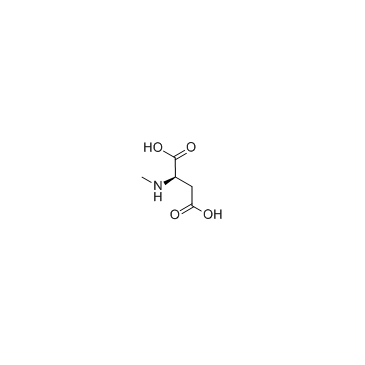 |
N-Methyl-D-aspartic acid
CAS:6384-92-5 |