| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
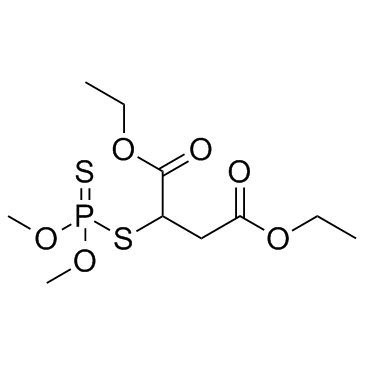 |
Malathion
CAS:121-75-5 |
|
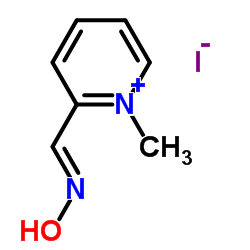 |
Pralidoxime Iodide
CAS:94-63-3 |
|
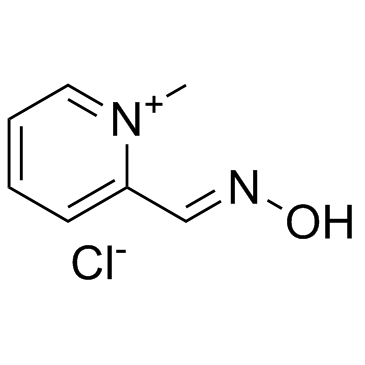 |
2-Pyridinealdoxime methochloride
CAS:51-15-0 |
|
 |
Native Electrophorus electricus (electric eel) Acetylcholinesterase
CAS:9000-81-1 |
|
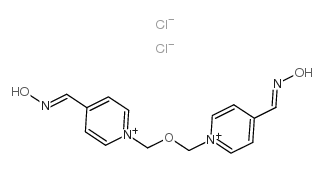 |
Obidoxime dichloride
CAS:114-90-9 |