| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
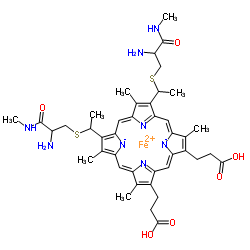 |
Cytochrome C
CAS:9007-43-6 |
|
 |
NAD+
CAS:53-84-9 |
|
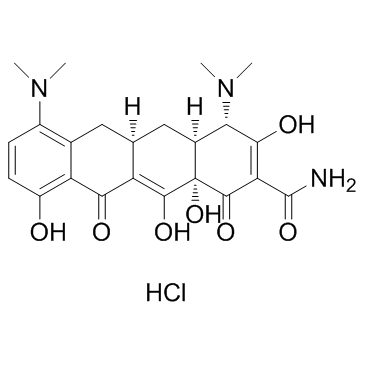 |
Minocycline hydrochloride
CAS:13614-98-7 |
|
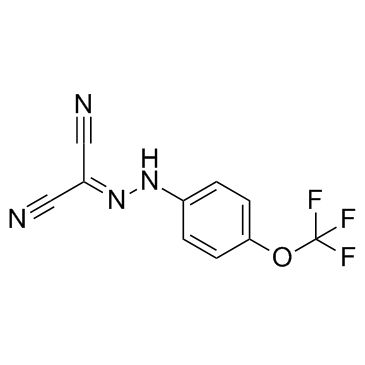 |
FCCP
CAS:370-86-5 |
|
 |
Alamethicin
CAS:27061-78-5 |