| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
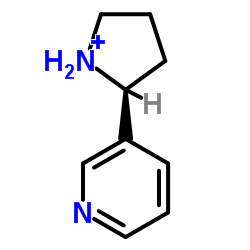 |
(±)-Nornicotine
CAS:5746-86-1 |
|
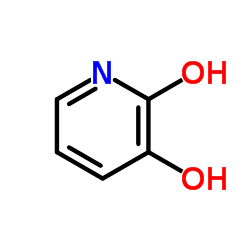 |
hydroxypyridone
CAS:16867-04-2 |
|
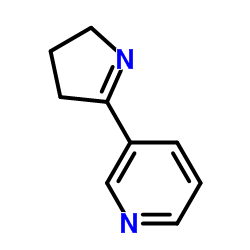 |
Myosmine
CAS:532-12-7 |