| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
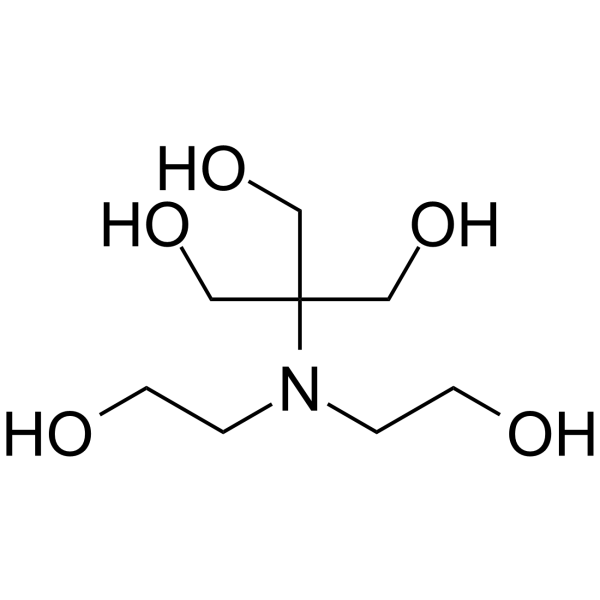 |
Bis-tris methane
CAS:6976-37-0 |
|
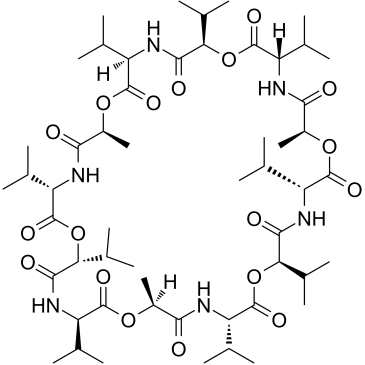 |
Valinomycin
CAS:2001-95-8 |
|
 |
L-Glutamine
CAS:56-85-9 |
|
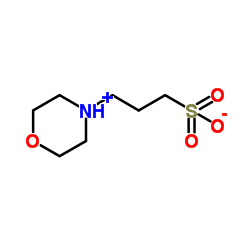 |
MOPS
CAS:1132-61-2 |
|
 |
4',6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride
CAS:28718-90-3 |
|
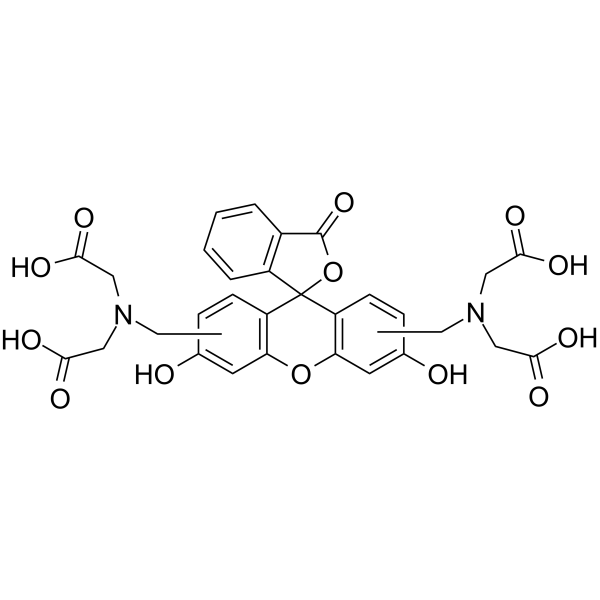 |
Calcein (mixture of isomers)
CAS:154071-48-4 |
|
 |
TMRM Perchlorate
CAS:115532-50-8 |
|
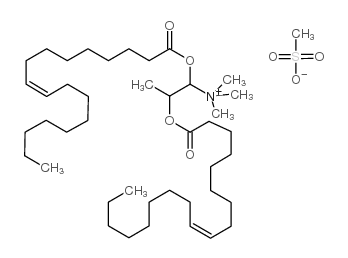 |
DOTAP Transfection Reagent
CAS:144189-73-1 |
|
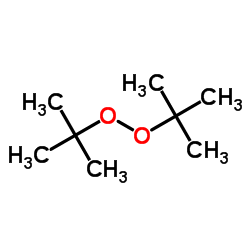 |
Di-tert-butyl peroxide
CAS:110-05-4 |
|
 |
2-Phenylindole
CAS:948-65-2 |