| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
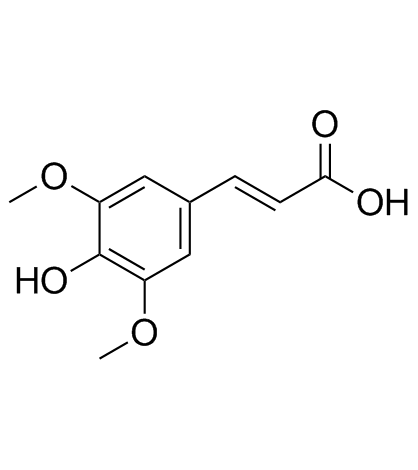 |
Sinapic acid
CAS:530-59-6 |
|
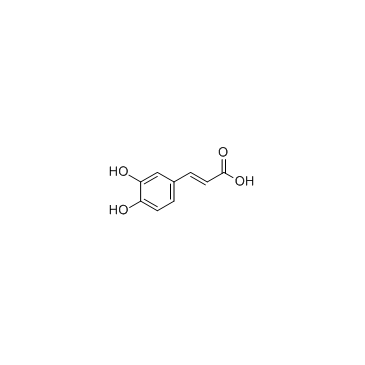 |
Caffeic acid
CAS:331-39-5 |
|
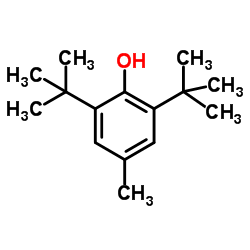 |
Butylated hydroxytoluene
CAS:128-37-0 |
|
 |
trans-4-Hydroxycinnamic acid
CAS:501-98-4 |
|
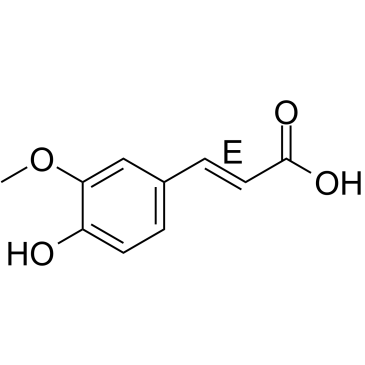 |
(E)-Ferulic acid
CAS:537-98-4 |
|
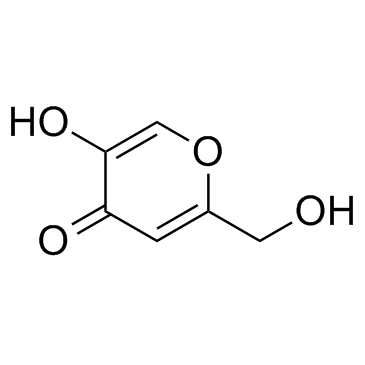 |
kojic acid
CAS:501-30-4 |
|
 |
Cinnamic acid
CAS:140-10-3 |
|
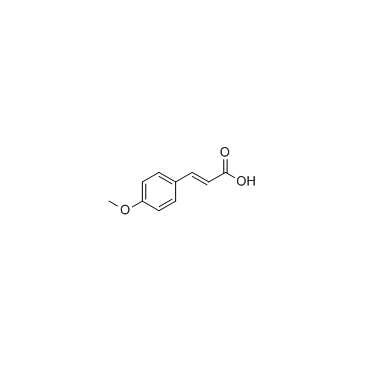 |
4-Methoxycinnamic acid
CAS:830-09-1 |
|
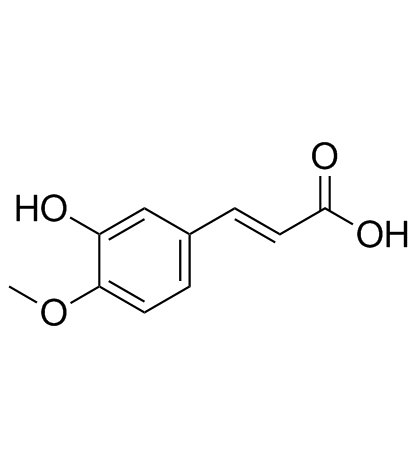 |
Isoferulic acid
CAS:537-73-5 |