| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
molecular iodine
CAS:7553-56-2 |
|
 |
tsh
CAS:9002-71-5 |
|
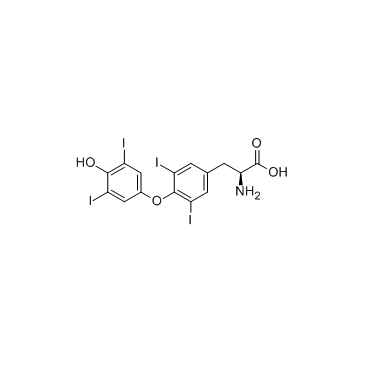 |
L-thyroxine
CAS:51-48-9 |