Factors implicated in the assessment of aminolevulinic acid-induced protoporphyrin IX fluorescence.
Beata Cunderlíková, Qian Peng, Anton Mateasík
Index: Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1830(3) , 2750-62, (2013)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Photodynamic therapy and photodiagnosis of cancer requires preferential accumulation of fluorescent photosensitizers in tumors. Clinical evidence documents feasibility of ALA-based photodiagnosis for tumor detection. However, false positive results and large variations in fluorescence intensities are also reported. Furthermore, selective accumulation of fluorescent species of photosensitizers in tumor cell lines, as compared to normal ones, when cultured in vitro, is not always observed. To understand this discrepancy we analyzed the impact of various factors on the intensity of detected PpIX fluorescence.Impacts of cell type, mitochondrial potential, cell-cell interactions and relocalization of PpIX among different cell types in co-cultures of different cell lines were analyzed by confocal microscopy and flow cytometry. Fluorescence spectroscopy was used to estimate absolute amounts of ALA-induced PpIX in individual cell lines. Immunofluorescence staining was applied to evaluate the ability of cell lines to produce collagen.Higher ALA-induced PpIX fluorescence in cancer cell lines as compared to normal ones was not detected by all the methods used. Mitochondrial activity was heterogeneous throughout the cell monolayers and could not be clearly correlated with PpIX fluorescence. Positive collagen staining was detected in all cell lines tested.Contrary to in vivo situation, ALA-induced PpIX production by cell lines in vitro may not result in higher PpIX fluorescence signals in tumor cells than in normal ones. We suggest that a combination of several properties of tumor tissue, instead of tumor cells only, is responsible for increased ALA-induced PpIX fluorescence in solid tumors.Understanding the reasons of increased ALA-induced PpIX fluorescence in tumors is necessary for reliable ALA-based photodiagnosis, which is used in various oncological fields.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
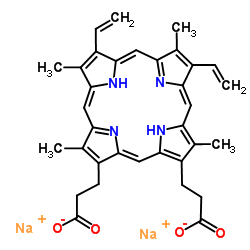 |
Disodium protoporphyrin IX
CAS:50865-01-5 |
C34H32N4Na2O4 |
|
Protein structure. Structure and activity of tryptophan-rich...
2015-01-30 [Science 347(6221) , 551-5, (2015)] |
|
Human PXR modulates hepatotoxicity associated with rifampici...
2013-04-01 [Nat. Med. 19(4) , 418-20, (2013)] |
|
Salicylic acid induces mitochondrial injury by inhibiting fe...
2013-12-01 [Mol. Pharmacol. 84(6) , 824-33, (2013)] |
|
Effects of 5-aminolevulinic acid-mediated photodynamic thera...
2013-10-01 [J. Surg. Res. 184(2) , 1013-21, (2013)] |
|
Measurement of the base number of DNA using a special callip...
2012-12-21 [Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 48(98) , 11990-2, (2012)] |