Effects of 5-aminolevulinic acid-mediated photodynamic therapy on antibiotic-resistant staphylococcal biofilm: an in vitro study.
Xin Li, Hao Guo, Qingzhong Tian, Gang Zheng, Yangchao Hu, Yu Fu, Honglue Tan
Index: J. Surg. Res. 184(2) , 1013-21, (2013)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Treatments of infections are not always successful because of multi-antibiotic-resistant organisms. It is therefore particularly urgent to provide more effective anti-infective strategy against these organisms. 5-Aminolevulinic acid (ALA), with the chemical structure C5H9NO3, is the only photodynamic therapy agent that is a biochemical precursor of a photosensitizer (protoporphyrin IX [PpIX]), which is naturally produced by the body. 5-Aminolevulinic acid-mediated photodynamic therapy (ALA-PDT) has been shown to have a strong effect on the treatment of localized cancerous and precancerous lesions, and further study demonstrated its efficacy for gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. However, its effect on biofilm formed by antibiotic-resistant strains has not been reported.In this study, we evaluated the effectiveness of ALA-PDT on biofilms formed by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 43300) and methicillin-resistant S epidermidis (MRSE 287). The strains were cultured with 40 mM of ALA in 24-well microtiter plates containing coverslips at 37°C for 24 h in the dark. PpIX fluorescence in biofilms formed by the two strains was observed by confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM). ALA-treated biofilms were irradiated at different doses (0, 100, 200, and 300 J/cm(2)) using a semiconductor laser. Biofilm exposed only to Tryptone Soy Broth or irradiation (300 J/cm(2)) was investigated. Viability determination, CLSM, and scanning electron microscopy were used to investigate the photodynamic inactivation of ALA-PDT.ALA was absorbed and converted to PpIX by both methicillin-resistant S aureus and methicillin-resistant S epidermidis. No cell inactivation was detectable in biofilms of either strain incubated with ALA without exposure to light, incubated with Tryptone Soy Broth only, or irradiated with red light only. However, a significant number of cells within biofilms were inactivated during irradiation with different doses of red light in the presence of 40 mM of ALA in a dose-dependent manner. The drastic reduction in cell survival within biofilms and the disruption of biofilms were confirmed by CLSM and scanning electron microscopy.ALA-PDT has the potential to eliminate the biofilm of Staphylococcus, especially antibiotic-resistant strains, effectively. It will be suitable for the treatment of superficial local infections such as surface wounds, burns, oral and dental infections, dermatologic infections such as acne and rosacea, and soft tissue and bone infections with bone exposure.Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
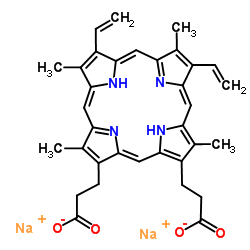 |
Disodium protoporphyrin IX
CAS:50865-01-5 |
C34H32N4Na2O4 | |
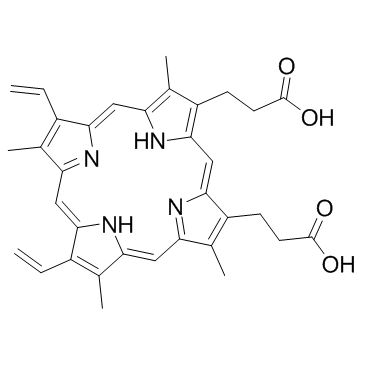 |
Protoporphyrin IX
CAS:553-12-8 |
C34H34N4O4 |
|
Protein structure. Structure and activity of tryptophan-rich...
2015-01-30 [Science 347(6221) , 551-5, (2015)] |
|
Human PXR modulates hepatotoxicity associated with rifampici...
2013-04-01 [Nat. Med. 19(4) , 418-20, (2013)] |
|
Salicylic acid induces mitochondrial injury by inhibiting fe...
2013-12-01 [Mol. Pharmacol. 84(6) , 824-33, (2013)] |
|
Measurement of the base number of DNA using a special callip...
2012-12-21 [Chem. Commun. (Camb.) 48(98) , 11990-2, (2012)] |
|
One divinyl reductase reduces the 8-vinyl groups in various ...
2013-01-01 [Plant Physiol. 161(1) , 521-34, (2013)] |