| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
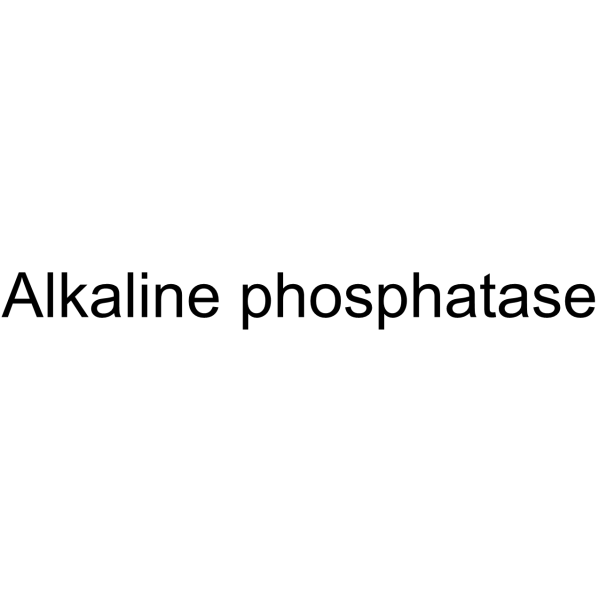 |
Native Bovine Alkaline Phosphatase
CAS:9001-78-9 |
|
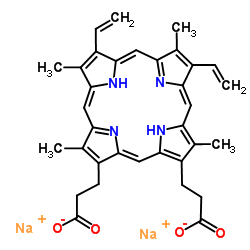 |
Disodium protoporphyrin IX
CAS:50865-01-5 |
|
 |
Isoniazid
CAS:54-85-3 |
|
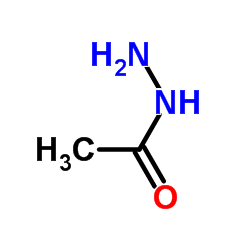 |
Acethydrazide
CAS:1068-57-1 |