| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
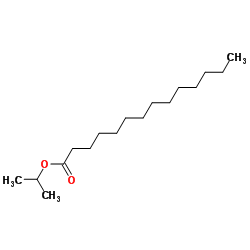 |
Isopropyl myristate
CAS:110-27-0 |
|
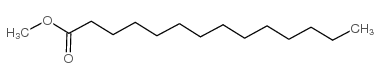 |
Methyl myristate
CAS:124-10-7 |
|
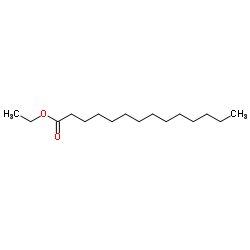 |
Ethyl tetradecanoate
CAS:124-06-1 |
|
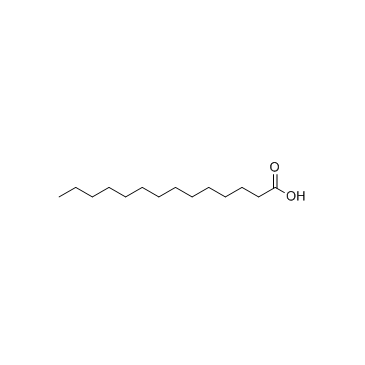 |
Myristic acid
CAS:544-63-8 |
|
 |
Ciprofloxacin
CAS:85721-33-1 |