| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
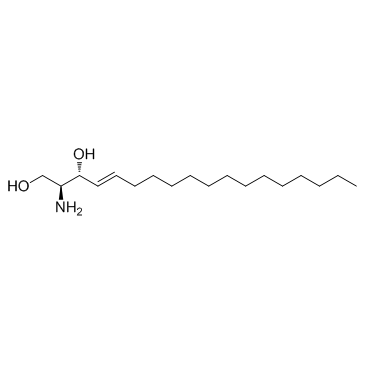 |
D-erythro-Sphingosine
CAS:123-78-4 |
|
 |
Sphingosine-1-phosphate
CAS:26993-30-6 |