| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
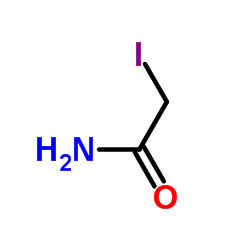 |
Iodoacetamide
CAS:144-48-9 |
|
 |
Lysozyme
CAS:12650-88-3 |
|
 |
1,4-Dithiothreitol
CAS:16096-97-2 |