| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
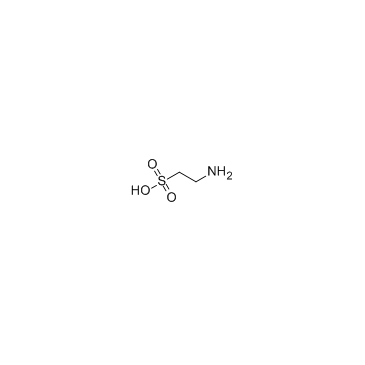 |
Taurine
CAS:107-35-7 |
|
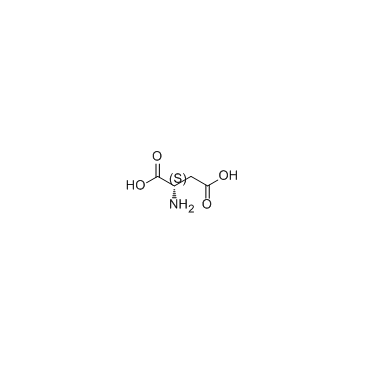 |
L-Aspartic acid
CAS:56-84-8 |
|
 |
4-Aminobutanoic acid
CAS:56-12-2 |
|
 |
L-Glutamine
CAS:56-85-9 |
|
 |
Glycine
CAS:56-40-6 |
|
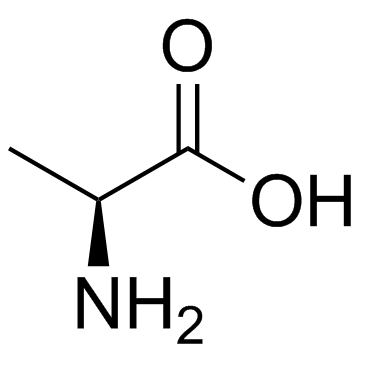 |
L-alanine
CAS:56-41-7 |
|
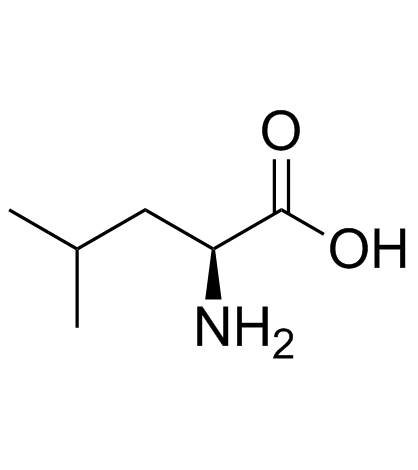 |
L-leucine
CAS:61-90-5 |
|
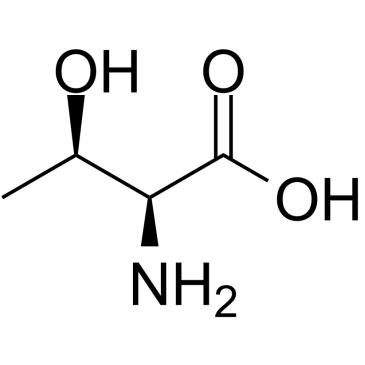 |
L-Threonine
CAS:72-19-5 |
|
 |
L-Isoleucine
CAS:73-32-5 |
|
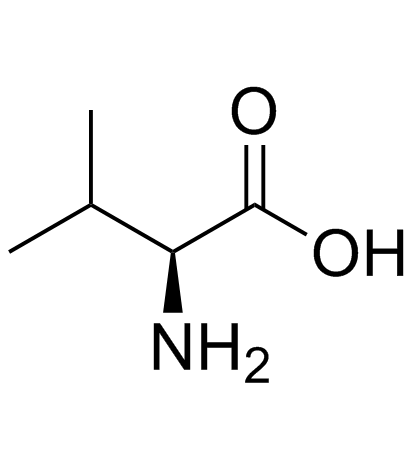 |
L-Valine
CAS:72-18-4 |