| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
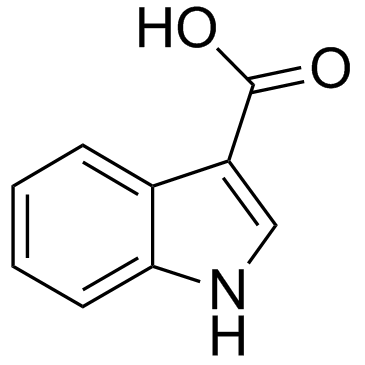 |
1H-Indole-3-carboxylic acid
CAS:771-50-6 |
|
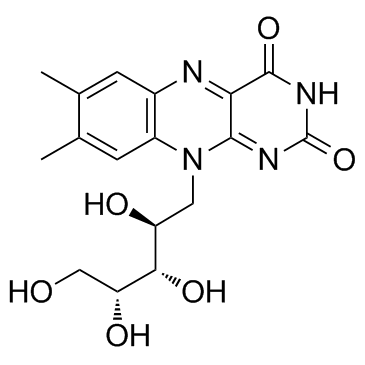 |
Riboflavine
CAS:83-88-5 |
|
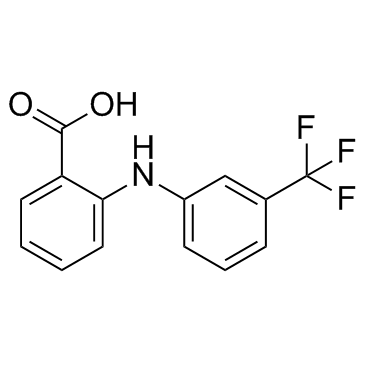 |
Flufenamic Acid
CAS:530-78-9 |
|
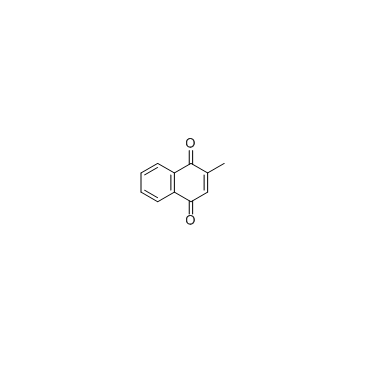 |
Menadione
CAS:58-27-5 |
|
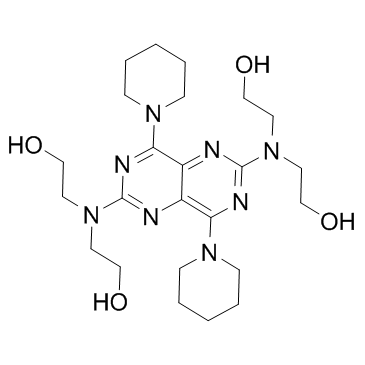 |
Dipyridamole
CAS:58-32-2 |
|
 |
liothyronine
CAS:6893-02-3 |
|
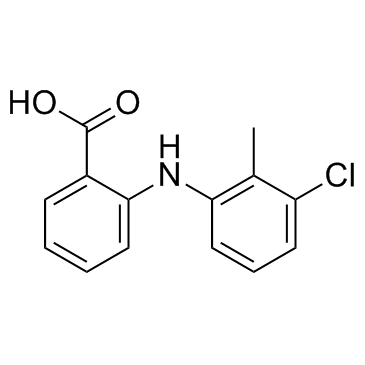 |
Tolfenamic acid
CAS:13710-19-5 |
|
 |
Tiratricol
CAS:51-24-1 |