| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Hydrochloric acid
CAS:7647-01-0 |
|
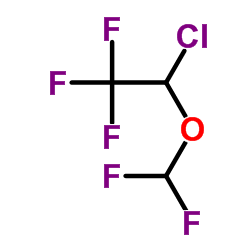 |
Isoflurane
CAS:26675-46-7 |
|
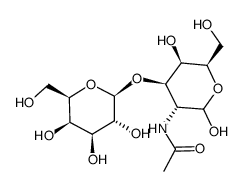 |
Galβ(1-3)GalNAc
CAS:20972-29-6 |
|
 |
4',6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole dihydrochloride
CAS:28718-90-3 |
|
 |
krypton-84
CAS:14993-91-0 |