| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Hydrochloric acid
CAS:7647-01-0 |
|
 |
L-(+)-Lysine monohydrochloride
CAS:657-27-2 |
|
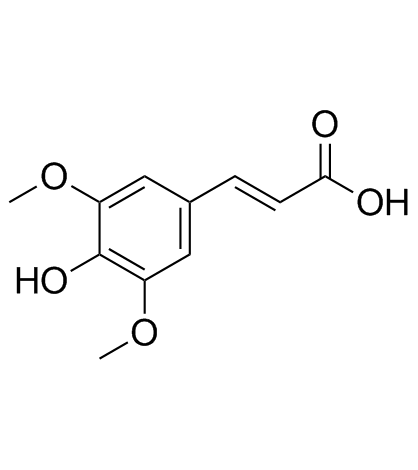 |
Sinapic acid
CAS:530-59-6 |
|
 |
dichloroethane
CAS:107-06-2 |
|
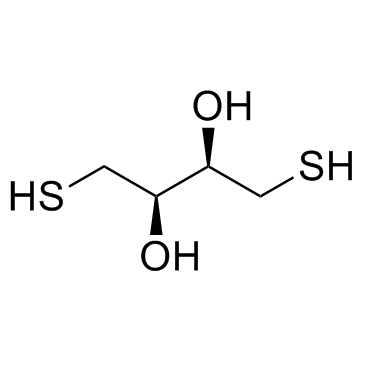 |
DL-Dithiothreitol
CAS:3483-12-3 |
|
 |
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
CAS:60-00-4 |
|
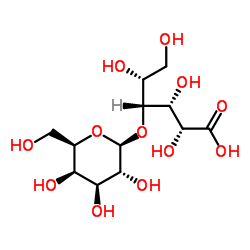 |
Lactobionic acid
CAS:96-82-2 |