| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Hydrochloric acid
CAS:7647-01-0 |
|
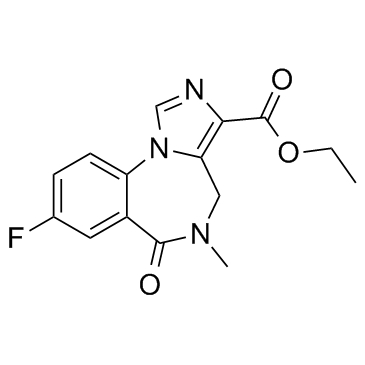 |
Flumazenil
CAS:78755-81-4 |
|
 |
Zolpidem
CAS:82626-48-0 |
|
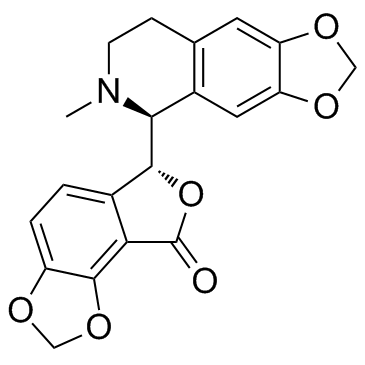 |
(+)-Bicuculline
CAS:485-49-4 |