| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
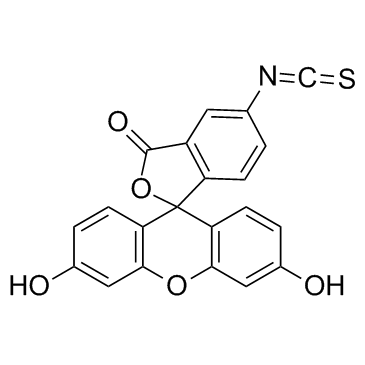 |
Fluorescein isothiocyanate
CAS:3326-32-7 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
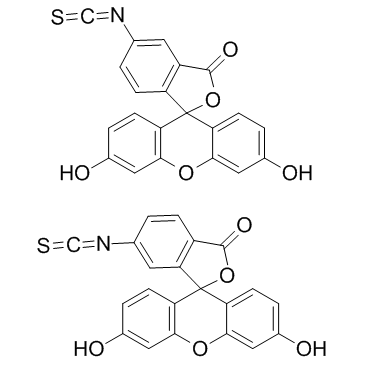 |
fluorescein 5-isothiocyanate
CAS:27072-45-3 |
|
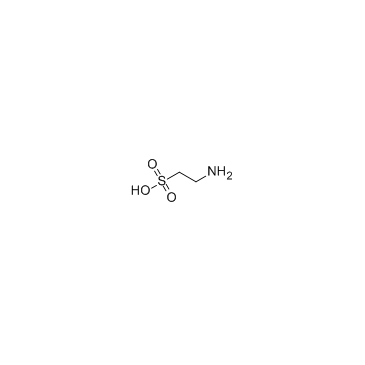 |
Taurine
CAS:107-35-7 |
|
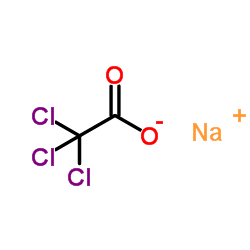 |
Sodium TCA
CAS:650-51-1 |
|
 |
Formaldehyde
CAS:50-00-0 |
|
 |
Sodium selenite
CAS:10102-18-8 |
|
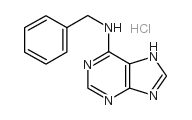 |
6-benzylaminopurine
CAS:162714-86-5 |
|
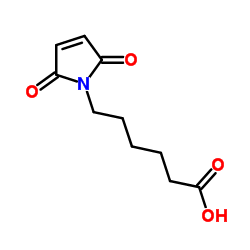 |
6-Maleimidocapronic acid
CAS:55750-53-3 |
|
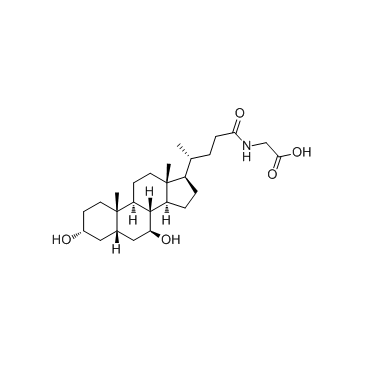 |
Glycoursodeoxycholic acid
CAS:64480-66-6 |