| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Formic Acid
CAS:64-18-6 |
|
 |
Docosanoic acid
CAS:112-85-6 |
|
 |
1-Bromohexane
CAS:111-25-1 |
|
 |
Lauric acid
CAS:143-07-7 |
|
 |
Decanoic acid
CAS:334-48-5 |
|
 |
Palmitic acid
CAS:57-10-3 |
|
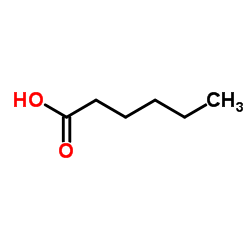 |
1-Hexanoic acid
CAS:142-62-1 |
|
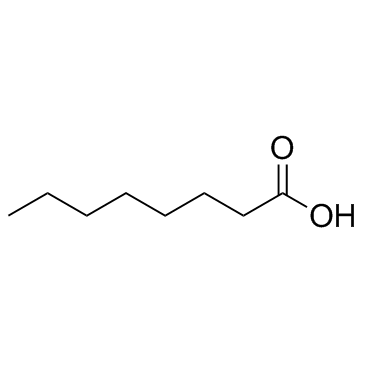 |
Octanoic acid
CAS:124-07-2 |
|
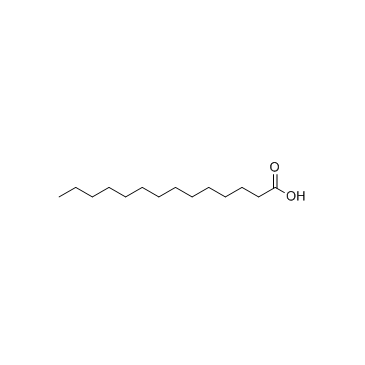 |
Myristic acid
CAS:544-63-8 |
|
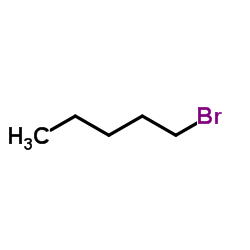 |
1-Bromopentane
CAS:110-53-2 |