| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Zinc
CAS:7440-66-6 |
|
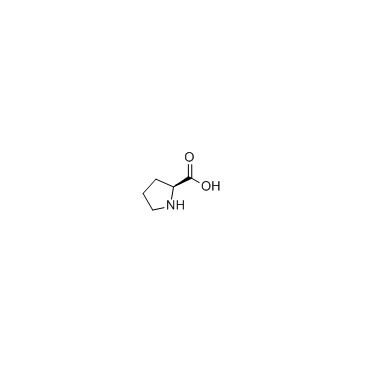 |
Proline
CAS:147-85-3 |
|
 |
p-Cresol
CAS:106-44-5 |
|
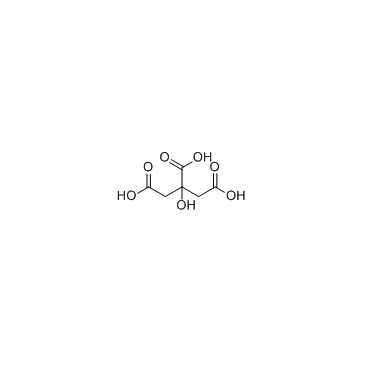 |
Citric Acid
CAS:77-92-9 |
|
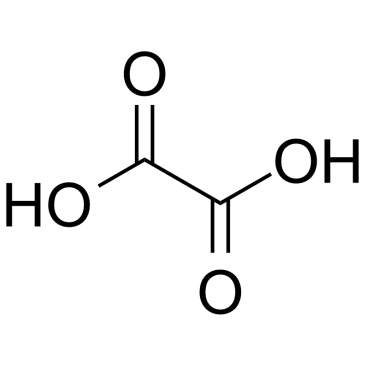 |
Oxalic acid
CAS:144-62-7 |
|
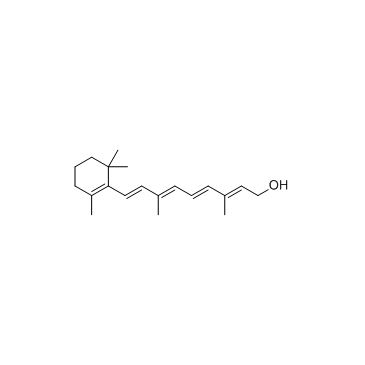 |
Vitamin A
CAS:68-26-8 |
|
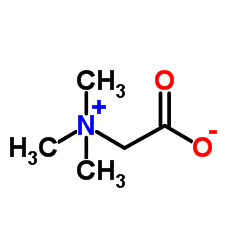 |
Betaine
CAS:107-43-7 |
|
 |
Xanthurenic acid
CAS:59-00-7 |
|
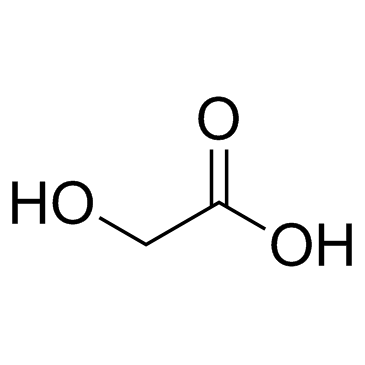 |
Glycolic acid
CAS:79-14-1 |
|
 |
L-Hydroxyproline
CAS:51-35-4 |