| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Acetonitrile
CAS:75-05-8 |
|
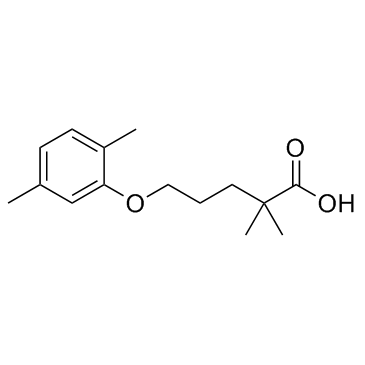 |
Gemfibrozil
CAS:25812-30-0 |
|
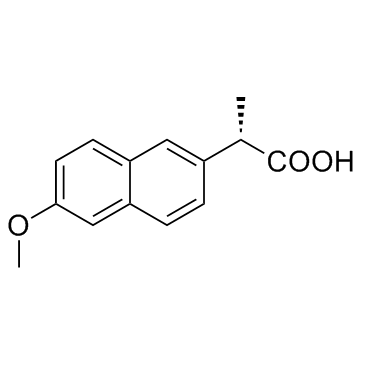 |
Naproxen
CAS:22204-53-1 |
|
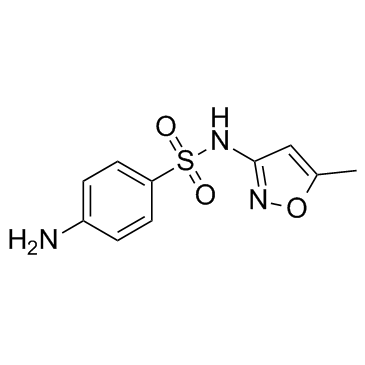 |
Sulfamethoxazole
CAS:723-46-6 |
|
 |
Ibuprofen
CAS:15687-27-1 |
|
 |
Caffeine
CAS:58-08-2 |
|
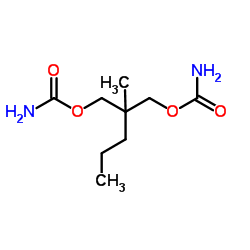 |
meprobamate
CAS:57-53-4 |
|
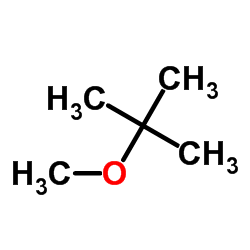 |
Methyl tert-butyl ether
CAS:1634-04-4 |
|
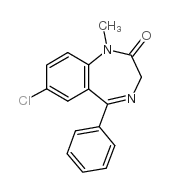 |
diazepam
CAS:439-14-5 |
|
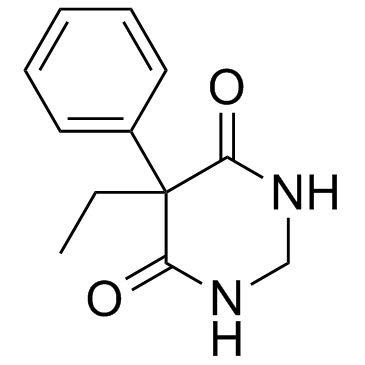 |
Primidone
CAS:125-33-7 |