| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Acetonitrile
CAS:75-05-8 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
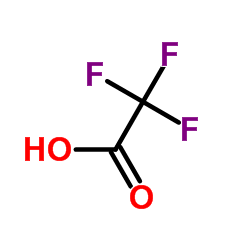 |
trifluoroacetic acid
CAS:76-05-1 |
|
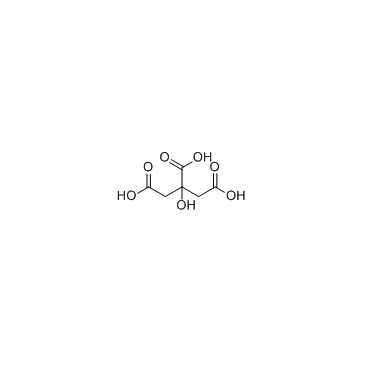 |
Citric Acid
CAS:77-92-9 |
|
 |
Fructose
CAS:57-48-7 |
|
 |
ethyl acetate
CAS:141-78-6 |
|
 |
L-Glutamine
CAS:56-85-9 |
|
 |
HEPES
CAS:7365-45-9 |
|
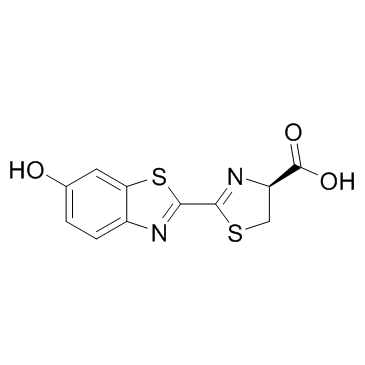 |
D-Luciferin
CAS:2591-17-5 |
|
 |
UNII:TF4710DNP9
CAS:5094-24-6 |