| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Acetonitrile
CAS:75-05-8 |
|
 |
Formic Acid
CAS:64-18-6 |
|
 |
Glutaric acid
CAS:110-94-1 |
|
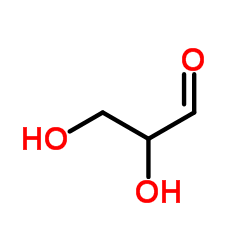 |
DL-Glyceric aldehyde
CAS:56-82-6 |
|
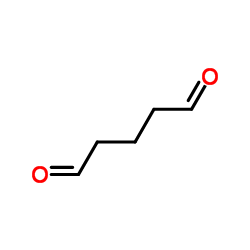 |
glutaraldehyde
CAS:111-30-8 |