| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
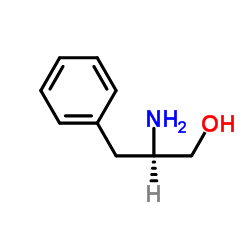 |
D-phenylalaninol
CAS:5267-64-1 |
|
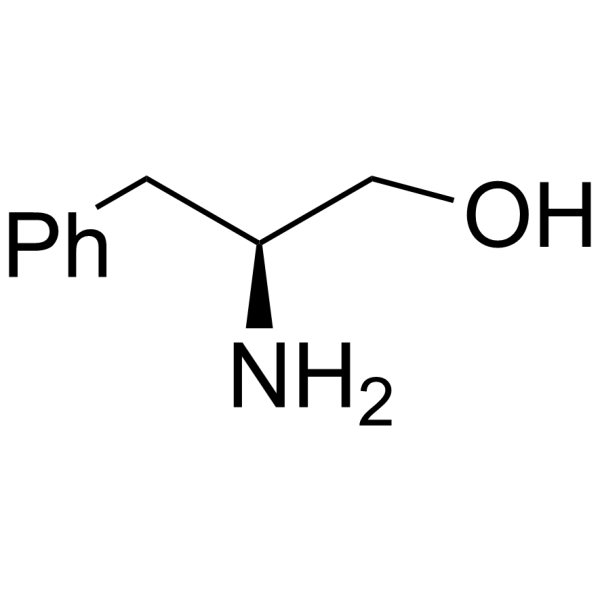 |
H-Phe-ol
CAS:3182-95-4 |
|
 |
Amino-2-propanol
CAS:78-96-6 |
|
 |
L-Alaninol
CAS:2749-11-3 |
|
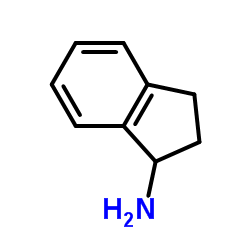 |
1-Indanamine
CAS:34698-41-4 |
|
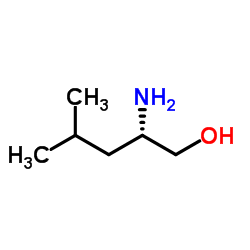 |
L-(+)-Leucinol
CAS:7533-40-6 |
|
 |
2-Anilinoethanol
CAS:122-98-5 |
|
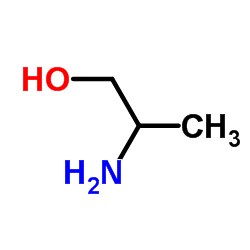 |
DL-Alaninol
CAS:6168-72-5 |