| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
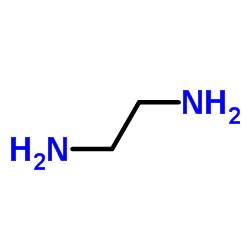 |
1,2-Ethanediamine
CAS:107-15-3 |
|
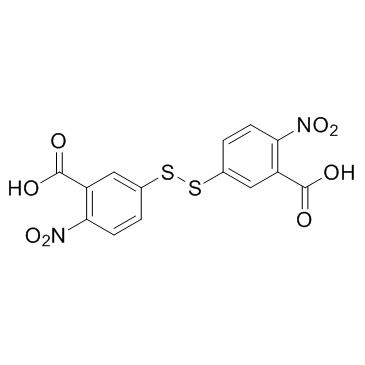 |
DTNB
CAS:69-78-3 |
|
 |
acetic acid
CAS:64-19-7 |
|
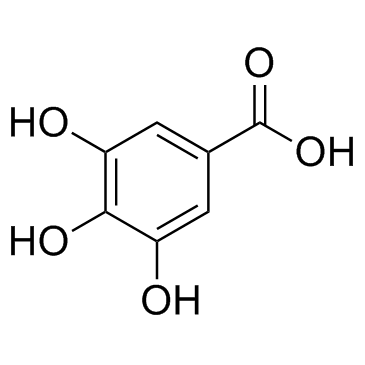 |
Gallic acid
CAS:149-91-7 |
|
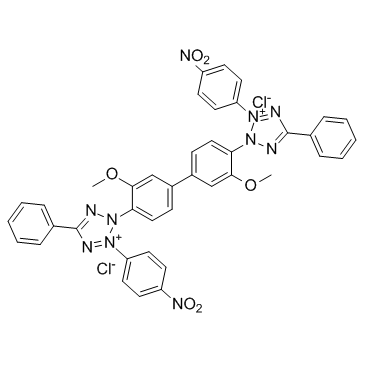 |
NBT
CAS:298-83-9 |
|
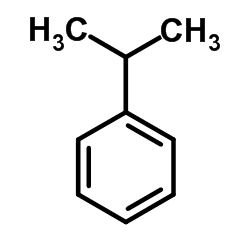 |
Cumene
CAS:98-82-8 |
|
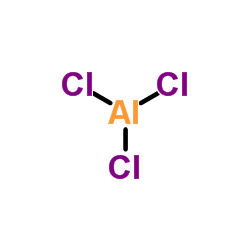 |
Aluminium chloride
CAS:7446-70-0 |
|
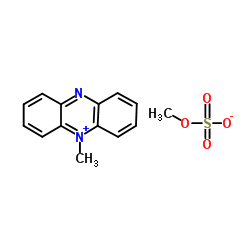 |
Phenazine methylsulfate
CAS:299-11-6 |
|
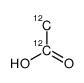 |
acetic acid
CAS:1173022-32-6 |
|
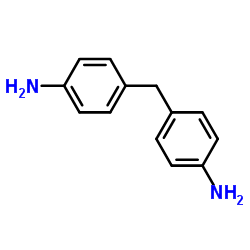 |
4,4′-methylenedianiline
CAS:101-77-9 |