| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
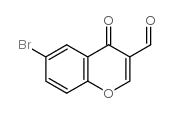 |
6-bromo-3-formylchromone
CAS:52817-12-6 |
|
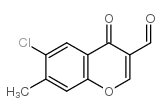 |
6-chloro-3-formyl-7-methylchromone
CAS:64481-12-5 |
|
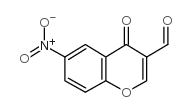 |
6-NITRO-4-OXO-4H-CHROMENE-3-CARBALDEHYDE
CAS:42059-80-3 |
|
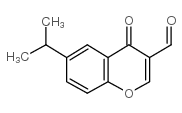 |
3-Formyl-6-isopropylchromone
CAS:49619-58-1 |
|
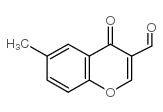 |
3-formyl-6-methylchromone
CAS:42059-81-4 |