| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
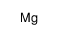 |
Magnesium
CAS:7439-95-4 |
|
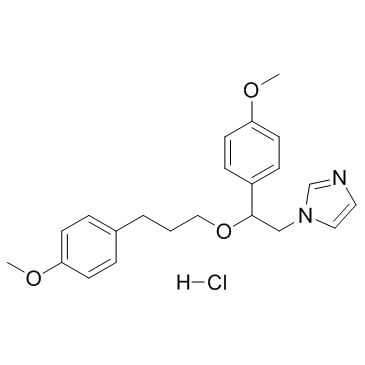 |
SKF-96365
CAS:130495-35-1 |
|
 |
sodium
CAS:7440-23-5 |
|
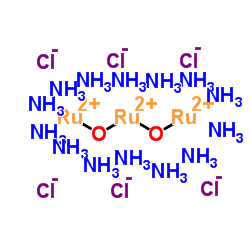 |
Ruthenium red
CAS:11103-72-3 |
|
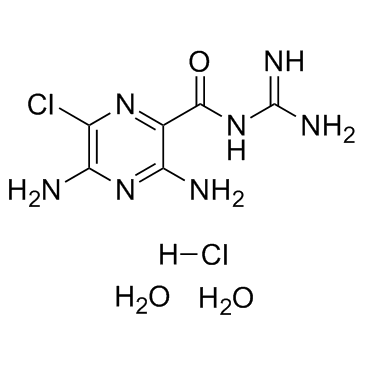 |
Amiloride HCl dihydrate
CAS:17440-83-4 |
|
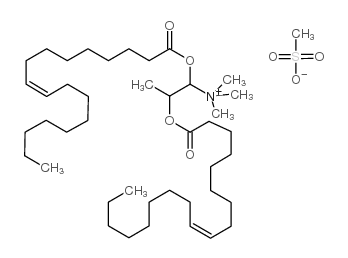 |
DOTAP Transfection Reagent
CAS:144189-73-1 |