| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
N-hexane
CAS:110-54-3 |
|
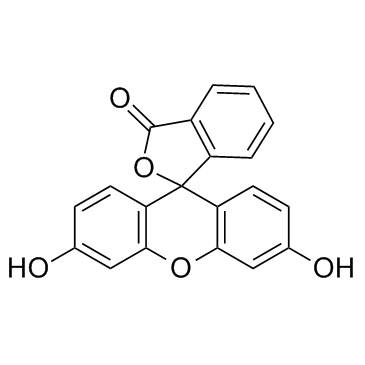 |
Fluorescein
CAS:2321-07-5 |
|
 |
Dichloromethane
CAS:75-09-2 |
|
 |
Ascorbic acid
CAS:50-81-7 |
|
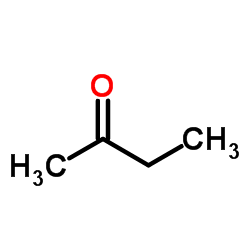 |
2-Butanone
CAS:78-93-3 |
|
 |
Cupric chloride
CAS:7447-39-4 |
|
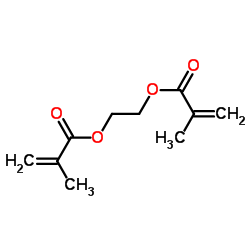 |
Ethylene methacrylate
CAS:97-90-5 |
|
 |
Iron(II,III) oxide
CAS:1317-61-9 |
|
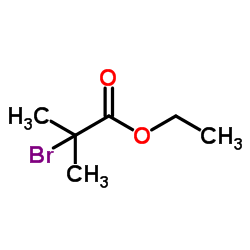 |
Ethyl 2-bromoisobutyrate
CAS:600-00-0 |
|
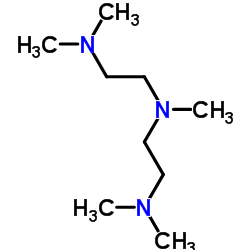 |
pentamethyldiethylenetriamine
CAS:3030-47-5 |