| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
N-hexane
CAS:110-54-3 |
|
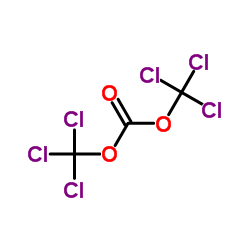 |
Triphosgene
CAS:32315-10-9 |
|
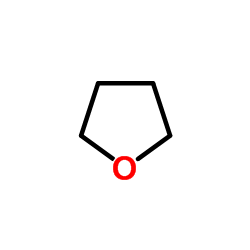 |
thf
CAS:109-99-9 |
|
 |
Boc-L-Proline
CAS:15761-39-4 |
|
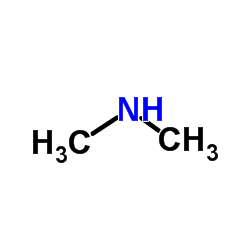 |
Dimethylamine
CAS:124-40-3 |
|
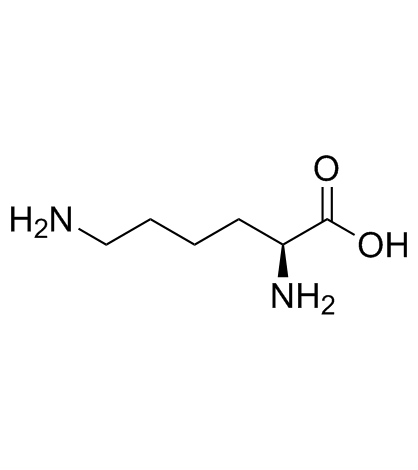 |
L-Lysine
CAS:56-87-1 |
|
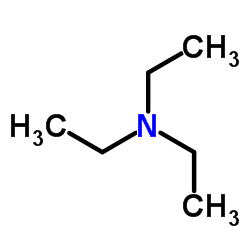 |
Triethylamine
CAS:121-44-8 |