| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
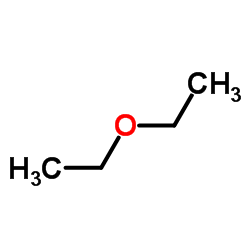 |
Diethyl ether
CAS:60-29-7 |
|
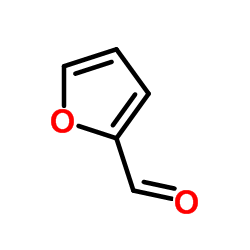 |
Furfural
CAS:98-01-1 |
|
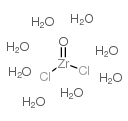 |
Zirconyl chloride octahydrate
CAS:13520-92-8 |
|
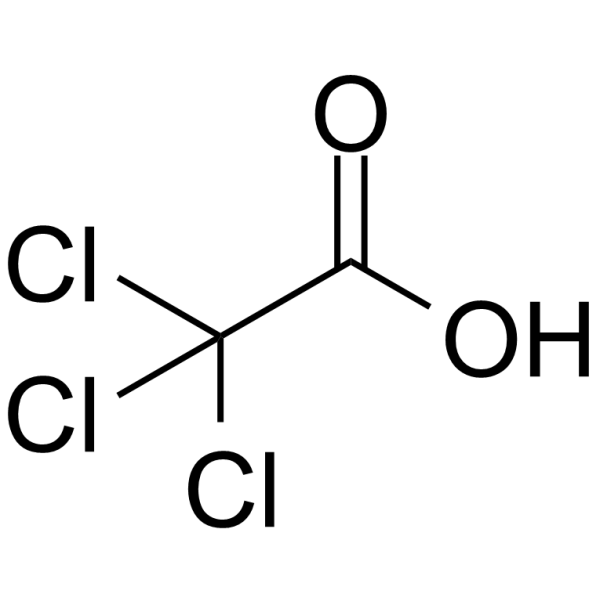 |
Trichloroacetic acid
CAS:76-03-9 |
|
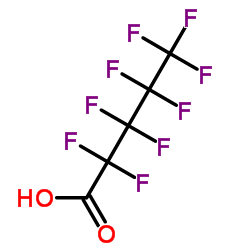 |
Perfluoropentanoic acid
CAS:2706-90-3 |