| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Potassium bromide
CAS:7758-02-3 |
|
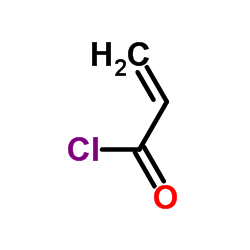 |
Acrylyl chloride
CAS:814-68-6 |
|
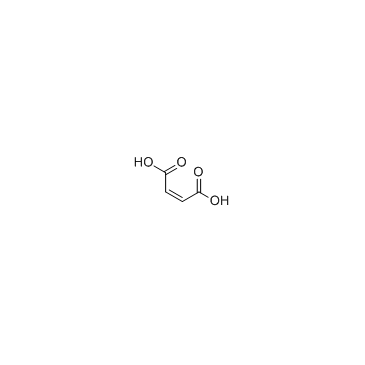 |
Maleic acid
CAS:110-16-7 |
|
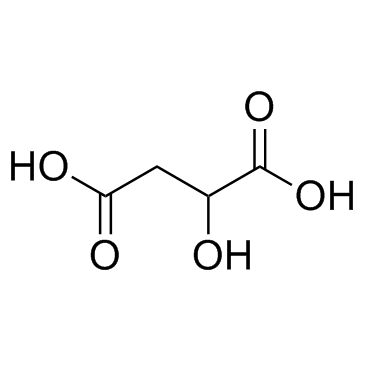 |
(±)-Malic Acid
CAS:6915-15-7 |
|
 |
Sodium Hypophosphite
CAS:7681-53-0 |