| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Acetone
CAS:67-64-1 |
|
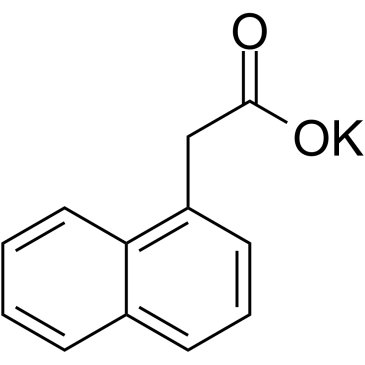 |
Potassium 1-naphthylacetate
CAS:15165-79-4 |
|
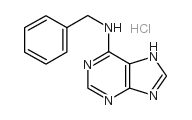 |
6-benzylaminopurine
CAS:162714-86-5 |
|
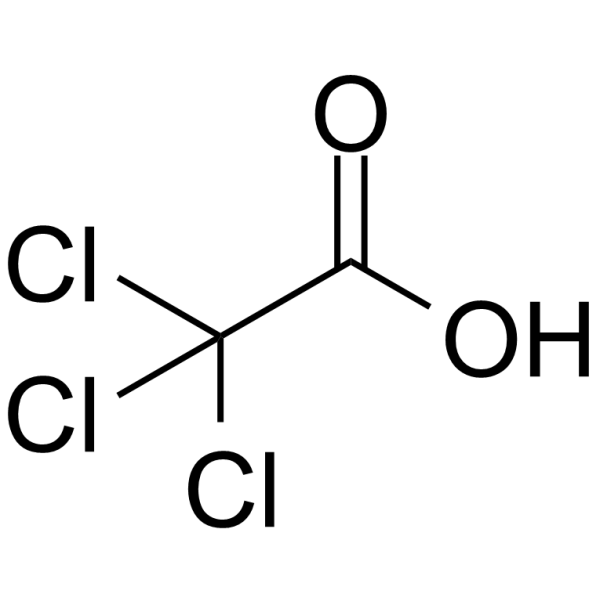 |
Trichloroacetic acid
CAS:76-03-9 |