| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Acetone
CAS:67-64-1 |
|
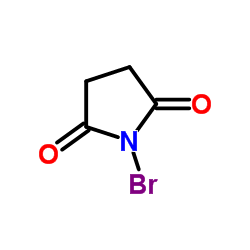 |
N-Bromosuccinimide
CAS:128-08-5 |
|
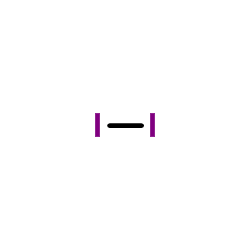 |
molecular iodine
CAS:7553-56-2 |
|
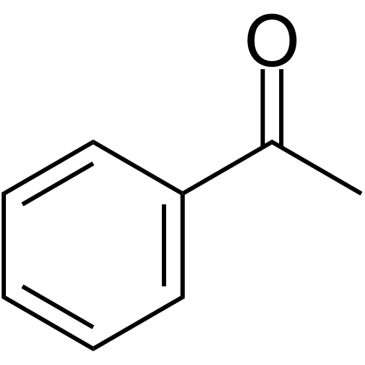 |
Acetophenone
CAS:98-86-2 |