| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Acetone
CAS:67-64-1 |
|
 |
N-hexane
CAS:110-54-3 |
|
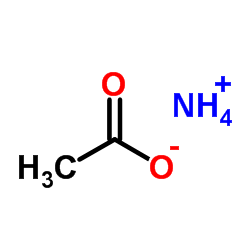 |
Ammonium acetate
CAS:631-61-8 |
|
 |
Acetonitrile
CAS:75-05-8 |
|
 |
Methanol
CAS:67-56-1 |
|
 |
Dichloromethane
CAS:75-09-2 |
|
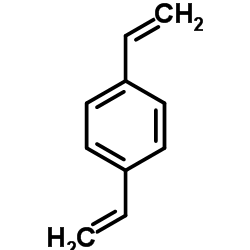 |
Divinylbenzene
CAS:1321-74-0 |
|
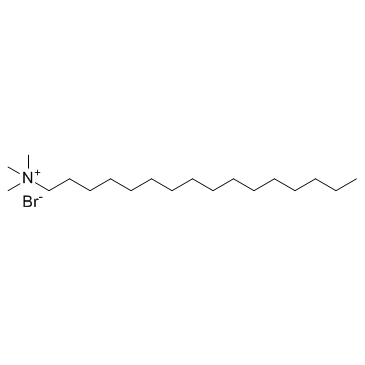 |
Hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide
CAS:57-09-0 |
|
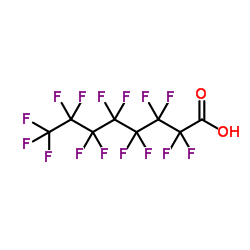 |
Perfluorooctanoic Acid
CAS:335-67-1 |
|
 |
3-Vinyl-2-pyrrolidinone
CAS:88-12-0 |