| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Ethanol
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
 |
Hydrochloric acid
CAS:7647-01-0 |
|
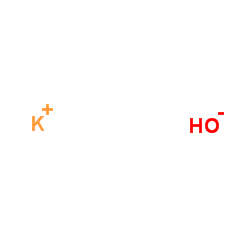 |
Potassium hydroxide
CAS:1310-58-3 |
|
 |
Aqueous ammonia
CAS:1336-21-6 |
|
 |
3-(Trimethoxysilyl)-1-propanamine
CAS:13822-56-5 |
|
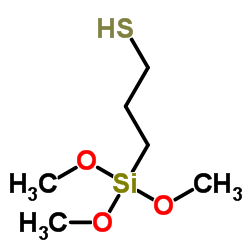 |
Trimethoxysilylpropanethiol
CAS:4420-74-0 |
|
 |
5-TAMRA-SE
CAS:150810-68-7 |
|
 |
DSP Crosslinker
CAS:57757-57-0 |