| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Ethanol
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
 |
Dichloromethane
CAS:75-09-2 |
|
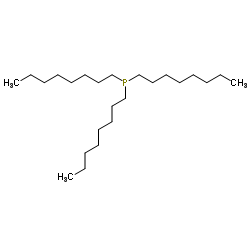 |
Trioctylphosphine
CAS:4731-53-7 |
|
 |
Selenium
CAS:7782-49-2 |
|
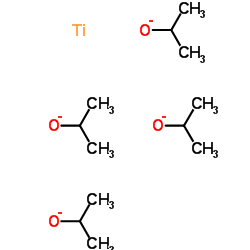 |
Titanium(4+) tetrapropan-2-olate
CAS:546-68-9 |
|
 |
acetic acid
CAS:64-19-7 |
|
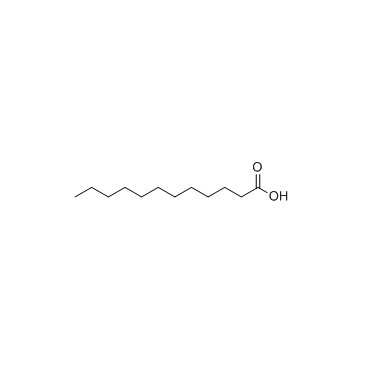 |
Lauric acid
CAS:143-07-7 |
|
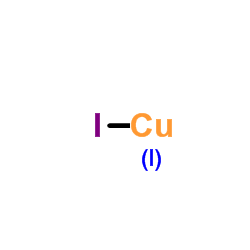 |
Copper(I) iodide
CAS:7681-65-4 |
|
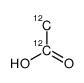 |
acetic acid
CAS:1173022-32-6 |
|
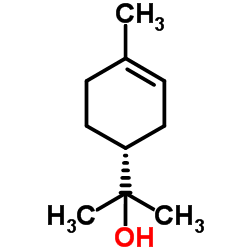 |
Terpineol
CAS:8000-41-7 |