| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Azocasein
CAS:102110-74-7 |
|
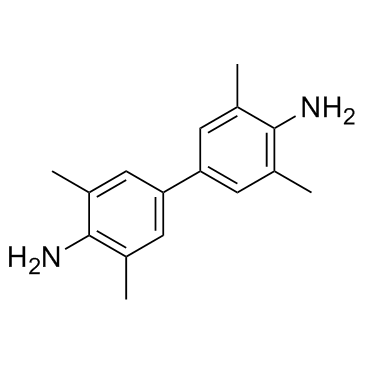 |
Tetramethylbenzidine
CAS:54827-17-7 |
|
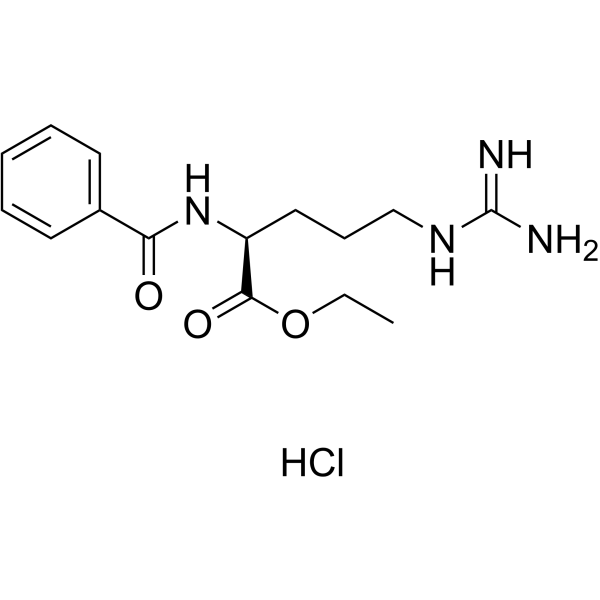 |
Bz-Arg-OEt��HCl
CAS:2645-08-1 |
|
 |
Sodium selenite
CAS:10102-18-8 |
|
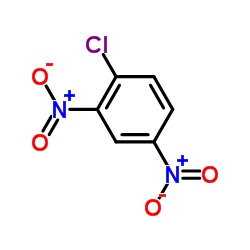 |
2,4-Dinitrochlorobenzene
CAS:97-00-7 |
|
 |
Glutathione
CAS:70-18-8 |
|
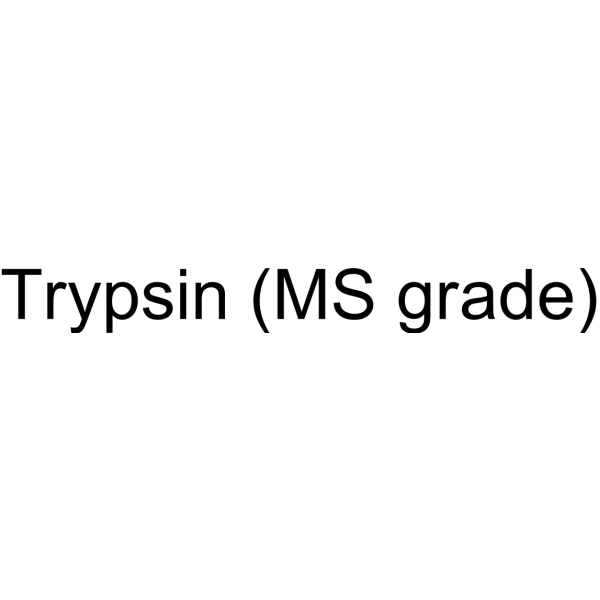 |
Trypsin
CAS:9002-07-7 |
|
 |
Tricaine methanesulfonate
CAS:886-86-2 |