| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
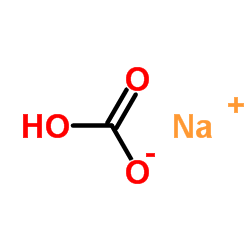 |
SodiuM bicarbonate
CAS:144-55-8 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
 |
Magnesium choride
CAS:7786-30-3 |
|
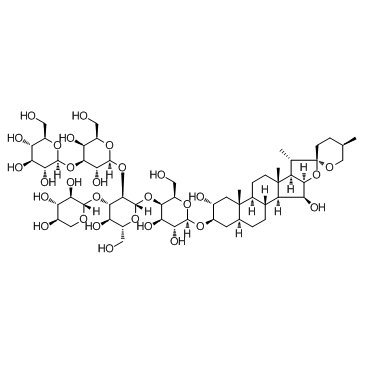 |
Digitonin
CAS:11024-24-1 |
|
 |
Tricaine methanesulfonate
CAS:886-86-2 |
|
 |
Melittin
CAS:20449-79-0 |
|
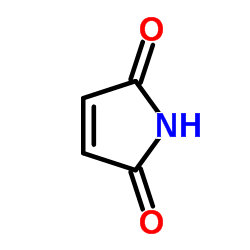 |
Maleimide
CAS:541-59-3 |