| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
Ethanol
CAS:64-17-5 |
|
 |
magnesium sulfate
CAS:7487-88-9 |
|
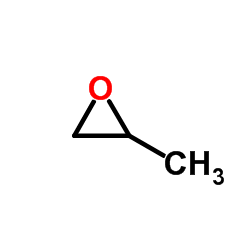 |
epoxypropane
CAS:75-56-9 |
|
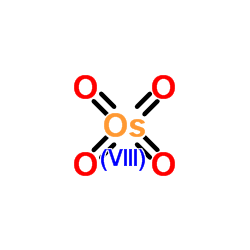 |
Osmium tetroxide
CAS:20816-12-0 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
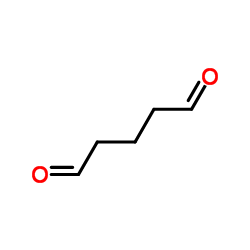 |
glutaraldehyde
CAS:111-30-8 |
|
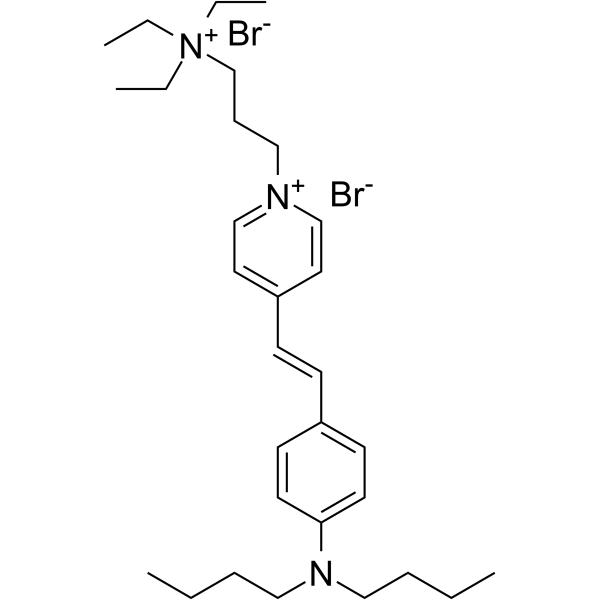 |
FM1-43
CAS:149838-22-2 |
|
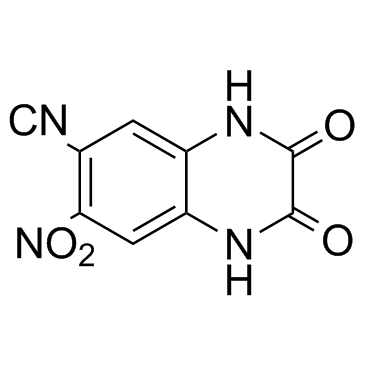 |
CNQX
CAS:115066-14-3 |