| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
sodium chloride
CAS:7647-14-5 |
|
 |
Acetonitrile
CAS:75-05-8 |
|
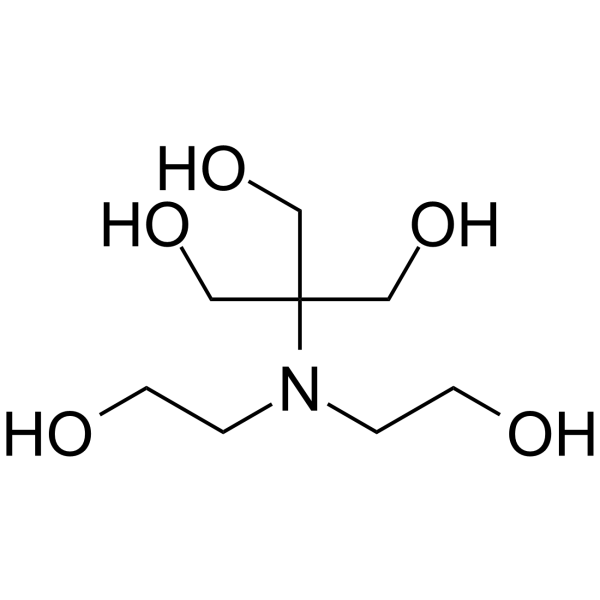 |
Bis-tris methane
CAS:6976-37-0 |
|
 |
SODIUM CHLORIDE-35 CL
CAS:20510-55-8 |
|
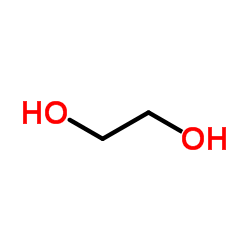 |
Ethylene glycol
CAS:107-21-1 |
|
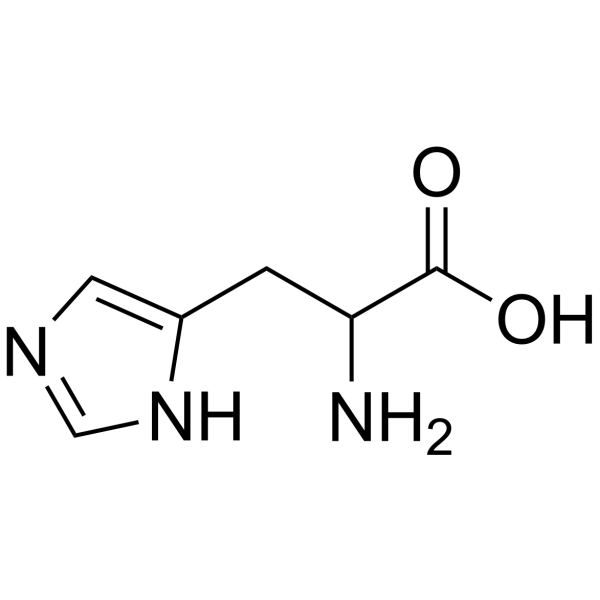 |
DL-Histidine
CAS:4998-57-6 |
|
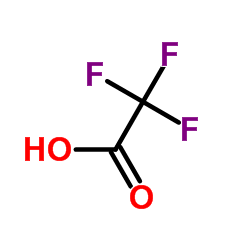 |
trifluoroacetic acid
CAS:76-05-1 |
|
 |
Fmoc-Ser(tBu)-OH
CAS:71989-33-8 |
|
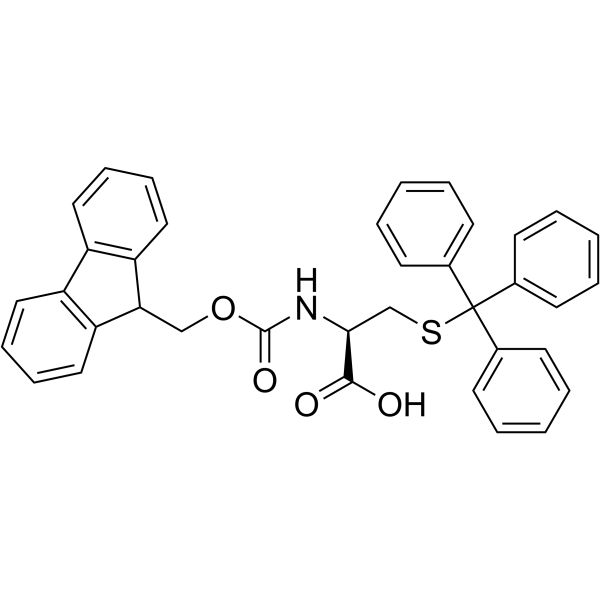 |
Fmoc-Cys(Trt)-OH
CAS:103213-32-7 |
|
 |
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
CAS:60-00-4 |