| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
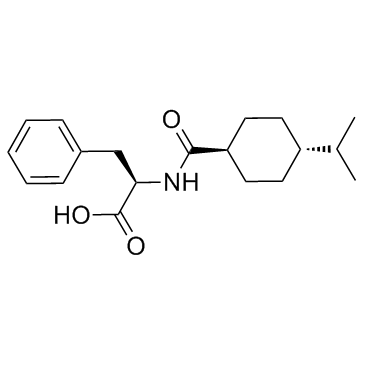 |
Nateglinide
CAS:105816-04-4 |
|
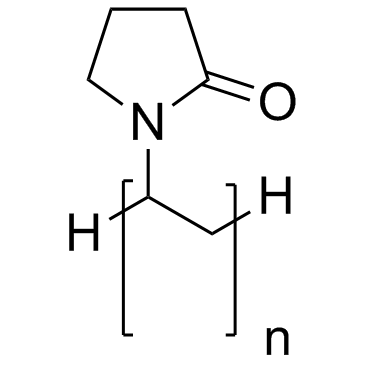 |
Polyvinylpyrrolidone
CAS:9003-39-8 |
|
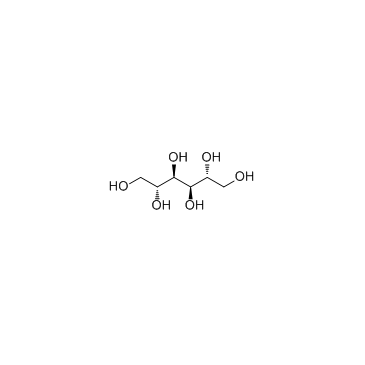 |
D-Mannitol
CAS:69-65-8 |
|
 |
Carboxymethyl cellulose
CAS:9004-32-4 |
|
![D-Phenylalanine, N-[[4-(1-methylethyl)cyclohexyl]carbonyl]-, cis Structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/221/105816-06-6.png) |
D-Phenylalanine, N-[[4-(1-methylethyl)cyclohexyl]carbonyl]-, cis
CAS:105816-06-6 |
|
 |
Sodium carboxyl methylstarch
CAS:9063-38-1 |